Introduction to Docker: A Beginner’s Guide
Introduction
Docker has revolutionized software development by making it easier to create, deploy, and manage applications in isolated environments called containers. Whether you're working on a small personal project or managing a large-scale enterprise application, Docker helps streamline development, testing, and deployment. This guide will introduce you to the core concepts of Docker, its components, and how to use it effectively.
Understanding Virtualization vs. Containerization
Before diving into Docker, it's important to understand how it differs from traditional virtualization.
What is Virtualization?
Virtualization involves creating multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server using a hypervisor (such as VMware, VirtualBox, or Hyper-V). Each VM has its own operating system, CPU allocation, memory, and storage.
What is Containerization?
Containerization allows multiple applications to run on a shared operating system while maintaining isolation from one another. Unlike VMs, containers do not require separate OS installations, making them lightweight and efficient.
Key Differences Between VMs and ContainersKey Differences Between VMs and Containers
-
VMs require a hypervisor; containers use the host OS kernel.
-
Containers start faster and use fewer system resources.
-
Containers provide better portability and scalability.
What is Docker?
Docker is an open-source platform that automates the deployment of applications inside lightweight, portable containers. It simplifies application deployment by eliminating inconsistencies between development, testing, and production environments.
Why Use Docker?
-
Portability: Containers work across different environments.
-
Scalability: Easily scale applications with container orchestration.
-
Efficiency: Uses fewer resources compared to VMs.
-
Consistency: Ensures that applications run the same way everywhere.

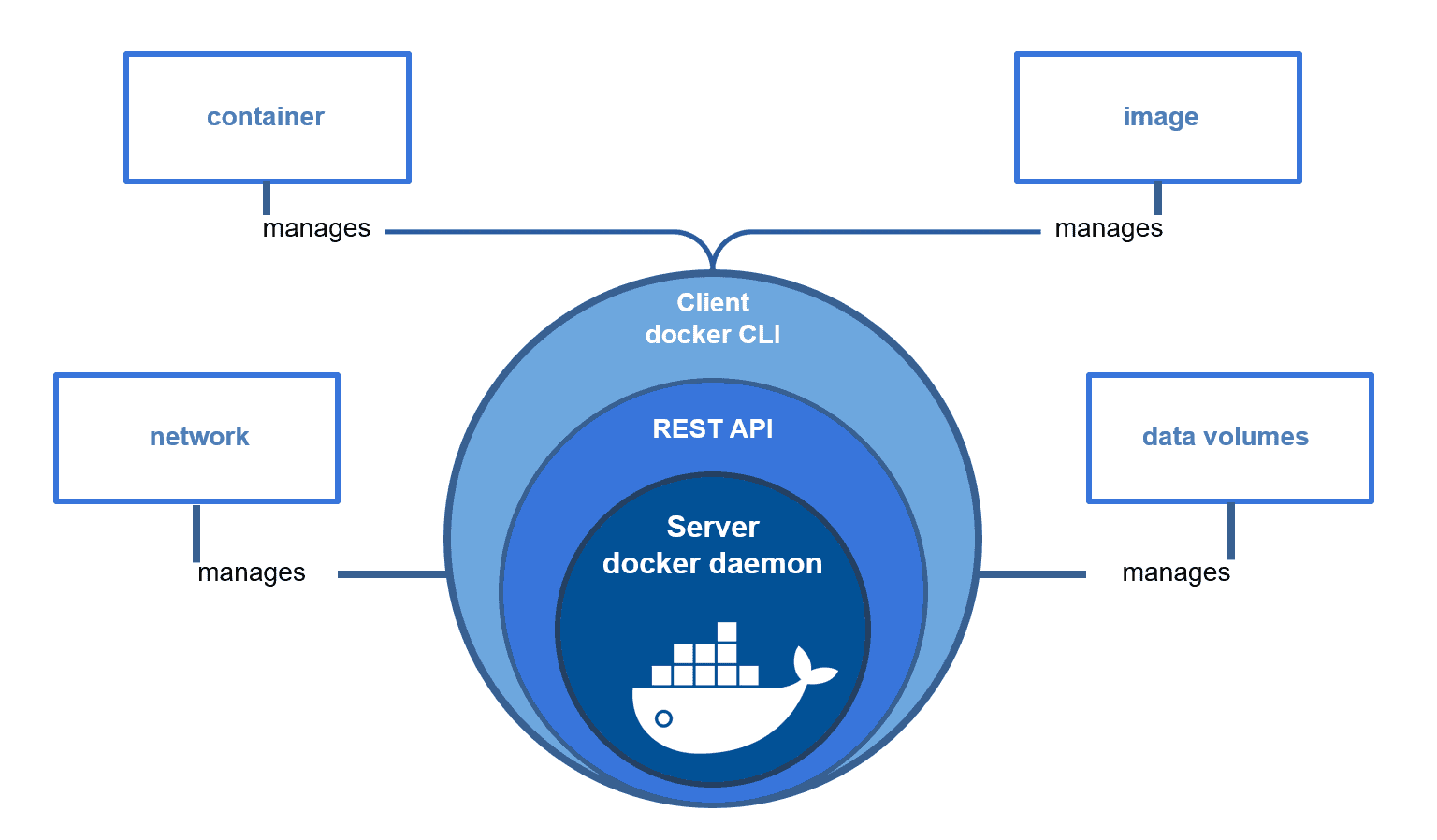
Key Components of Docker
Dockerfile
A Dockerfile is a script containing instructions for creating a Docker image. It specifies dependencies, configuration settings, and commands to execute inside a container.
Docker Image
A Docker image is a blueprint of an application that includes all dependencies, libraries, and system configurations. Images are immutable, meaning they do not change once created.
Docker Container
A Docker container is a runnable instance of an image. Multiple containers can be launched from the same image and can be run independently or interact with each other.
Docker Installation and Setup
Installing Docker
-
Docker can be installed on various operating systems:
-
Windows & macOS: Download Docker Desktop from Docker's official website
Linux (Ubuntu Example):
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker.io -y
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable docker**Verifying Installation
Run the following command to check if Docker is installed:
docker --version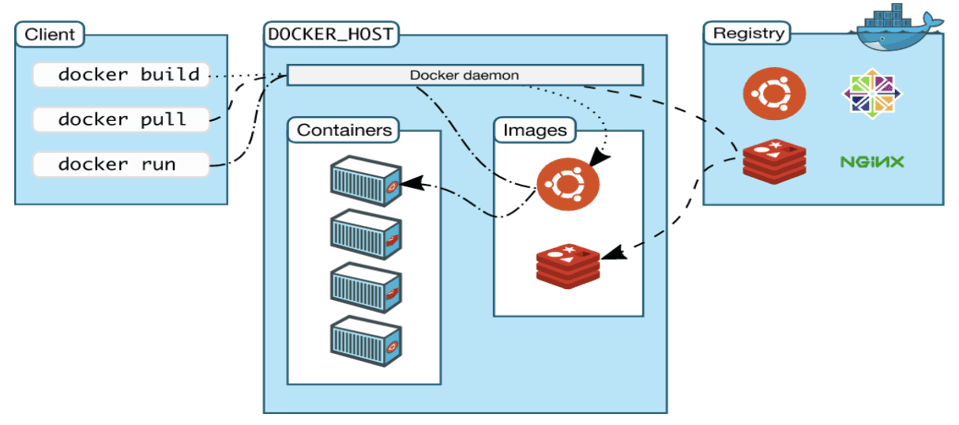
Working with Docker Images
Pulling an Image from Docker Hub
Docker Hub is a public repository for Docker images. To pull an image:
docker pull ubuntu:latestBuilding a Docker Image
Create a Dockerfile with the following content:
FROM ubuntu:latest
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y figlet
CMD ["figlet", "Hello, Docker!"]Build the image:
docker build -t my-ubuntu .Listing Available Images
docker imagesRunning and Managing Docker Containers
Running a Container
docker run my-ubuntuListing Running Containers
docker psStopping and Removing Containers
docker stop <container_id>
docker rm <container_id>
Docker Hub – The Public Image Repository
Docker Hub provides pre-built images that can be used as the foundation for custom applications.
Searching for Images on Docker Hub
docker search nginxPulling and Using an Image
docker pull nginx
docker run -d -p 8080:80 nginxWriting a Simple Dockerfile
Here's an example of a simple Dockerfile that creates a container with an Ubuntu base:
FROM ubuntu:latest
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y curl
CMD ["echo", "Hello from Docker!"]Build and run the image:
docker build -t my-container .
docker run my-containerDocker Networking Basics
Containers can communicate with each other using Docker networking features.
Listing Networks
docker network lsCreating a Network
docker network create my_networkConnecting Containers to a Network
docker network connect my_network my-containerDocker Volumes – Managing Data Persistence
By default, Docker containers do not persist data when stopped.
Creating and Using a Volume
docker volume create my_volume
docker run -v my_volume:/data ubuntuListing Volumes
docker volume lsBest Practices for Using Docker
-
Use small base images (e.g., alpine) to reduce image size.
-
Keep Dockerfiles simple and readable.
-
Tag images properly for version control.
-
Use multi-stage builds to optimize image size.
Docker in CI/CD Pipelines
Docker is widely used in CI/CD pipelines to ensure consistent builds and deployments.
Using Docker in GitHub Actions
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Build Docker image
run: docker build -t my-app .
- name: Run container
run: docker run my-appCommon Docker Commands Cheat Sheet
docker pull <image>
docker build -t <image_name> .
docker run -d -p 8080:80 <image>
docker ps -a
docker stop <container_id>
docker rm <container_id>
docker rmi <image_id>
Conclusion
Docker simplifies the development and deployment of applications by providing a lightweight, reproducible environment. By mastering Docker images, containers, and networking, you can streamline your workflow and ensure consistency across different environments.
FAQs
-
What is the main benefit of Docker?Docker enables consistent environments across development, testing, and production.
-
How is Docker different from a virtual machine?Docker containers share the host OS kernel, whereas VMs require a separate OS.
-
Can I run multiple containers from the same image?Yes, multiple containers can be created from the same image.
-
What is Docker Compose?Docker Compose is a tool for managing multi-container applications using a YAML file.
-
Is Docker free to use?Yes, Docker has a free community edition, with additional features in the enterprise version.