Roni McGuinness

AI Agents and the Rise of Agentic AI
Evolution of Agentic AI
The evolution of agentic AI represents a significant leap in artificial intelligence, transforming simple programs into autonomous, decision-making entities.
This journey began in the mid-20th century with the advent of cybernetics and early AI research. Alan Turing's exploration of machine intelligence and Norbert Wiener's work on feedback systems laid the groundwork for systems capable of autonomous action
Early AI systems, such as expert systems in the 1970s and 1980s, hinted at agentic capabilities, though they were limited by computational power and rigid programming frameworks
The 2000s
Brought significant advancements in machine learning techniques, particularly neural networks and reinforcement learning. These methods enabled AI systems to learn from data and refine their decision-making processes, paving the way for more sophisticated agentic AI.
The integration of agentic AI into robotics and autonomous systems, such as self-driving vehicles, showcased the potential of AI agents to navigate and interact with real-world environments.
Recent years agentic AI:
The has been dramatic shift in the capabilities of agentic AI driven by breakthroughs in Deep learning and large language models. Systems like GPT-4 demonstrate strong generative abilities and can engage in complex reasoning tasks.
-
This has led to the development of AI copilots and assistants that can understand language, set goals autonomously, and make adaptive choices in real-time.
-
Industry leaders like OpenAI, Allen Institute for AI, and Moveworks are pushing the boundaries of agentic AI, creating systems that can reliably manage complex goals and workflows across varied domains with minimal human oversight
-
As we move forward, the focus is shifting towards creating AI agents that not only respond to commands but also proactively collaborate with humans, adapting to changing circumstances and making complex decisions in professional and creative fields.
From Simple Scripts to Autonomous Partners

Fundamentals
The fundamentals begin with perception. An AI agent must first understand its world, whether that's a virtual environment, a dataset, or the physical realm through sensors. This perception forms the foundation for everything that follows - like a chef first surveying their kitchen before beginning to cook. The agent processes this input through sophisticated models, weighing options and considering consequences, much as a chess player thinks several moves ahead.
Truth
What truly sets agentic AI apart is its capacity for autonomous decision-making. These systems don't simply follow predetermined paths; they adapt and respond to changing circumstances. Consider how a modern AI assistant might not just answer questions, but ask for clarification, suggest alternatives, or even decline requests that conflict with its objectives. This represents a fundamental shift from tools we use to partners we collaborate with.
Implications
The implications ripple outward. In business, agentic AI systems already manage complex logistics, trade stocks, and handle customer service with increasing sophistication. In research, they design experiments and generate hypotheses. In creative fields, they function as collaborators, offering novel perspectives and solutions. Each advancement brings us closer to artificial general intelligence - systems that can match and potentially exceed human capabilities across diverse domains.
Tool Control
AI agents are made from decision-making architectures, input output and are not deterministic, by a program per se. As these agents grow more capable, questions of control, alignment, and ethics move from philosophical musings to practical imperatives. How do we ensure these digital beings remain aligned with human values while preserving their autonomous capabilities? The answer lies not in constraint, but in careful design and clear principles - like teaching a child right from wrong while nurturing their independence.
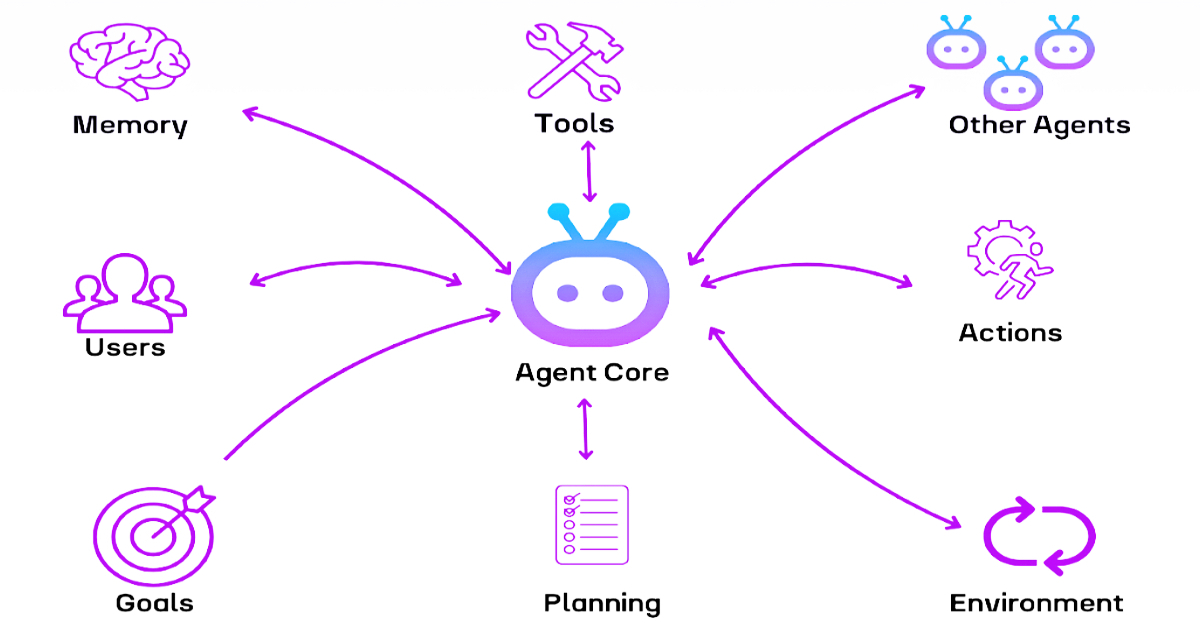
In the realm of artificial intelligence, a quiet revolution unfolds.
AI agents - software programs endowed with the ability to perceive, decide, and act - mark humanity's first steps toward creating truly autonomous digital entities.
Unlike traditional programs that merely respond to commands, these agents observe their environment, form goals, and take actions to achieve them. Think of an AI agent as a digital being with a mission, equipped with both a map and a compass.
AI Agents: leveraging AI models like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Co-pilot and Jasper.ai . They can automate tasks for businesses, offering solutions for:
-
AI Data Visualization: Creating infographics to simplify complex data and make it understandable for a wider audience.
-
AI Website Building: Building websites for new businesses, particularly LLCs
-
Marketing: Personalizing content and improving conversion rates. "with marketing driven AI agents
-
Sales: Analyzing lead scores and prioritizing high-potential leads.
-
Analytics: Helping you focusing on the right kind of campaingns and customers to increase Leads.
Part II Understanding AI Agents From the Ground Up
The Architecture of Intelligence: The back story that led to Neural Networks & Agentic AI begins in Part II